

Y = #sqrt(x+2) - 7# First, make a prediction.will the graph be translated right 2 or left 2, up 7 or down 7?įind the domain by setting x + 2 #>=# 0 for starters.Īnd, subtraction of 7, must mean down 7. If you are ready for a challenge, we can try to translate in more than one direction at a time! Adding 3 will raise the graph up, and subtracting 4 will lower the graph by 4 units. Here are the steps that are useful in graphing any. The addition or subtraction on the OUTSIDE of the square root function will cause the graph to translate up or down. We have seen how to graph the parent square root function f(x) x. Now, let's explore how to translate a square root function vertically. The principal square root function - the inverse of the square of x (quadratic) function.

And then it will be easy for us to do it. And if we need to calculate the side of a square-shaped plot of 100 square meters, what do we use The square root, of course. This graph will be translated 5 units to the left. The square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the legs in a right-angled triangle. This means that you need to hold down your ALT key and press the numbers 2, 5, and 1 on the numeric keypad. Now repeat for x + 5 #>=# 0, or #x >= -5#. Below is the keyboard shortcut to insert a square root symbol in a cell in Excel: ALT + 251. This implies a horizontal shift/translation of 2 units to the right. You must set x - 2 #>=# 0, or say that you understand that the square root function has a domain of #x>=2#. Let's look at the effect of the addition or subtraction.
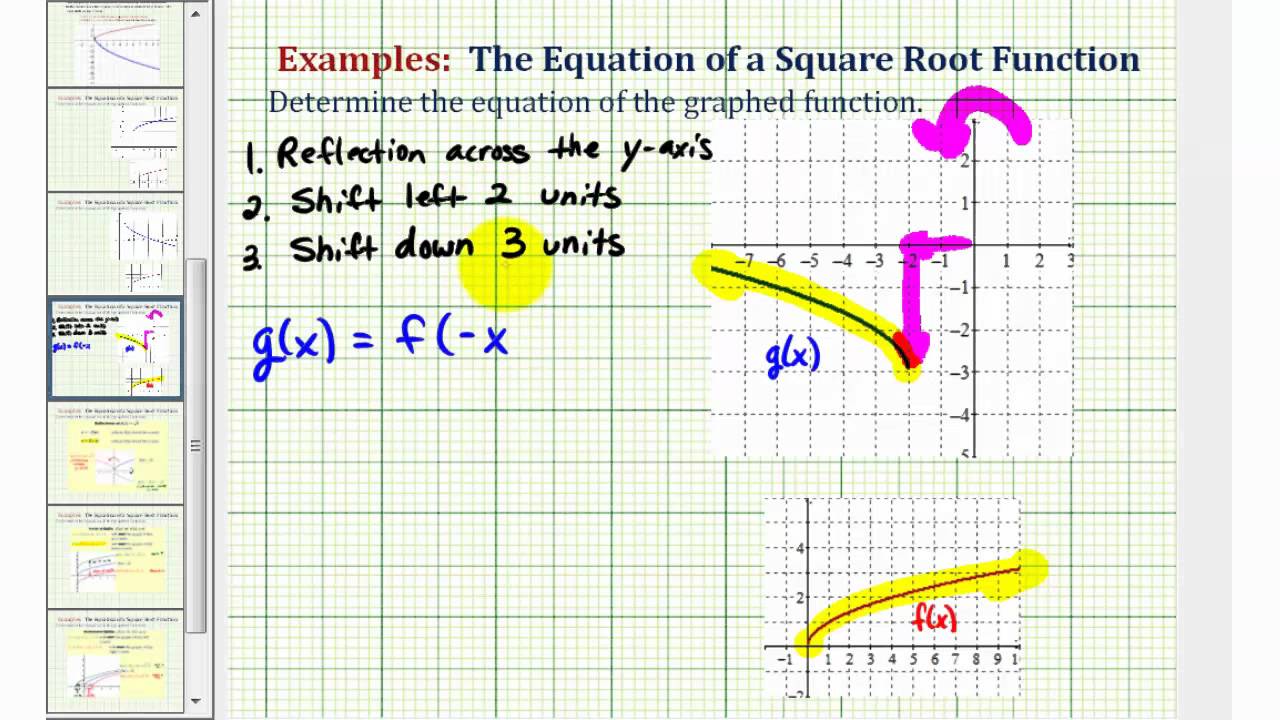
In the case of the square root function, it would look like y = #sqrt(x-2)# or y = #sqrt(x+5)#. In order to translate any function to the right or left, place an addition or subtraction "inside" of the Parent function.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
